React 基础渲染流程
基于 v19.2.0 版本
本文通过下述 Demo 分析 React v19.2.0 的基础渲染流程。
import { createRoot } from 'react-dom/client'
function App() {
return (
<div>
<h1>基础渲染流程</h1>
<p>观察 createRoot 和首次渲染的执行过程</p>
</div>
)
}
// 断点 1: createRoot 调用前
debugger;
const root = createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
// 断点 2: render 调用前
debugger;
root.render(<App />);
export default App
创建阶段
从 Demo 中可以看出,初始化流程主要分为两个步骤:
1. createRoot()
2. render(<App />)
本文会按照 React 代码的执行顺序进行分析。在稍后会给出适当的更高层级的抽象说明。本着自底向上的方式逐步分析理解 React 的渲染流程。
createRoot() 创建 FiberRootNode 和 ReactDomRoot 对象实例
createRoot 方法关键逻辑如下:
// packages/react-dom/src/client/ReactDOMRoot.js
export function createRoot(
container: Element | Document | DocumentFragment,
options?: CreateRootOptions,
): RootType {
if (!isValidContainer(container)) {
throw new Error('Target container is not a DOM element.');
}
warnIfReactDOMContainerInDEV(container);
const concurrentUpdatesByDefaultOverride = false;
let isStrictMode = false;
let identifierPrefix = '';
let onUncaughtError = defaultOnUncaughtError;
let onCaughtError = defaultOnCaughtError;
let onRecoverableError = defaultOnRecoverableError;
let onDefaultTransitionIndicator = defaultOnDefaultTransitionIndicator;
let transitionCallbacks = null;
if (options !== null && options !== undefined) {
if (options.unstable_strictMode === true) {
isStrictMode = true;
}
if (options.identifierPrefix !== undefined) {
identifierPrefix = options.identifierPrefix;
}
if (options.onUncaughtError !== undefined) {
onUncaughtError = options.onUncaughtError;
}
if (options.onCaughtError !== undefined) {
onCaughtError = options.onCaughtError;
}
if (options.onRecoverableError !== undefined) {
onRecoverableError = options.onRecoverableError;
}
if (enableDefaultTransitionIndicator) {
if (options.onDefaultTransitionIndicator !== undefined) {
onDefaultTransitionIndicator = options.onDefaultTransitionIndicator;
}
}
if (options.unstable_transitionCallbacks !== undefined) {
transitionCallbacks = options.unstable_transitionCallbacks;
}
}
const root = createContainer(
container,
ConcurrentRoot,
null,
isStrictMode,
concurrentUpdatesByDefaultOverride,
identifierPrefix,
onUncaughtError,
onCaughtError,
onRecoverableError,
onDefaultTransitionIndicator,
transitionCallbacks,
);
markContainerAsRoot(root.current, container);
const rootContainerElement: Document | Element | DocumentFragment =
!disableCommentsAsDOMContainers && container.nodeType === COMMENT_NODE
? (container.parentNode: any)
: container;
listenToAllSupportedEvents(rootContainerElement);
// $FlowFixMe[invalid-constructor] Flow no longer supports calling new on functions
return new ReactDOMRoot(root);
}
在程序执行时,container 参数的值是 DOM Element 对象即 document.getElementById('root') 获取到的 div#root。
createRoot 方法内部调用 createFiberRoot(container),然后返回 new FiberRootNode() 创建的 FiberRoot 实例。之后通过 createHostRootFiber 创建 HostRootFiber,它是宿主树的根节点。
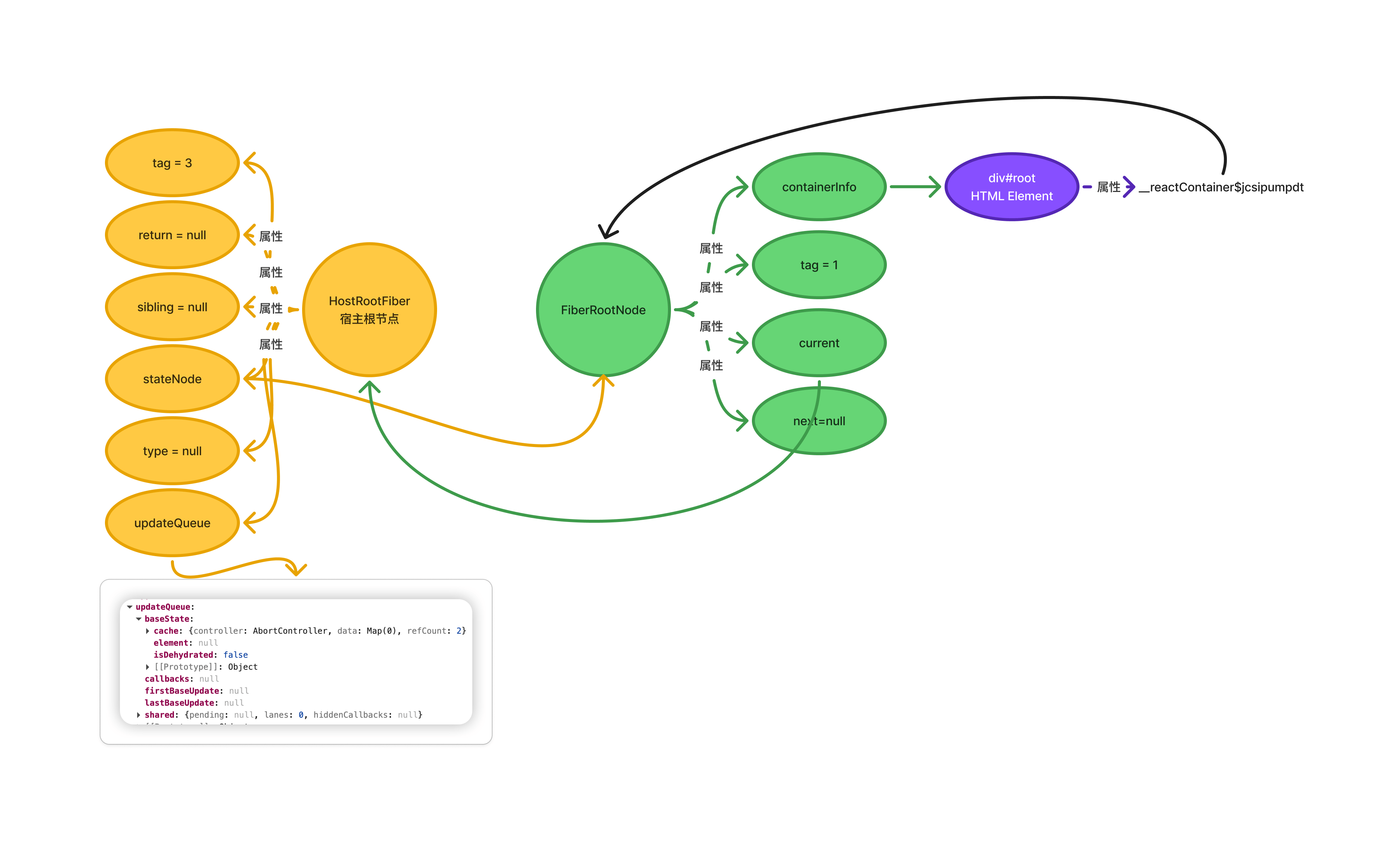
创建根 Fiber 后,通过 new ReactDOMRoot() 实例化一个对象,此对象有如下几个属性:
1. _internalRoot 属性的值是 FiberRootNode
2. render 方法
3. unmount 方法
其中 render 和 unmount 方法挂在 prototype 上面。
render() 开启 Fiber 构建之路
由于 root.render(<App />) 的执行,所以会先创建 App 的 ReactElement 节点。如下图:
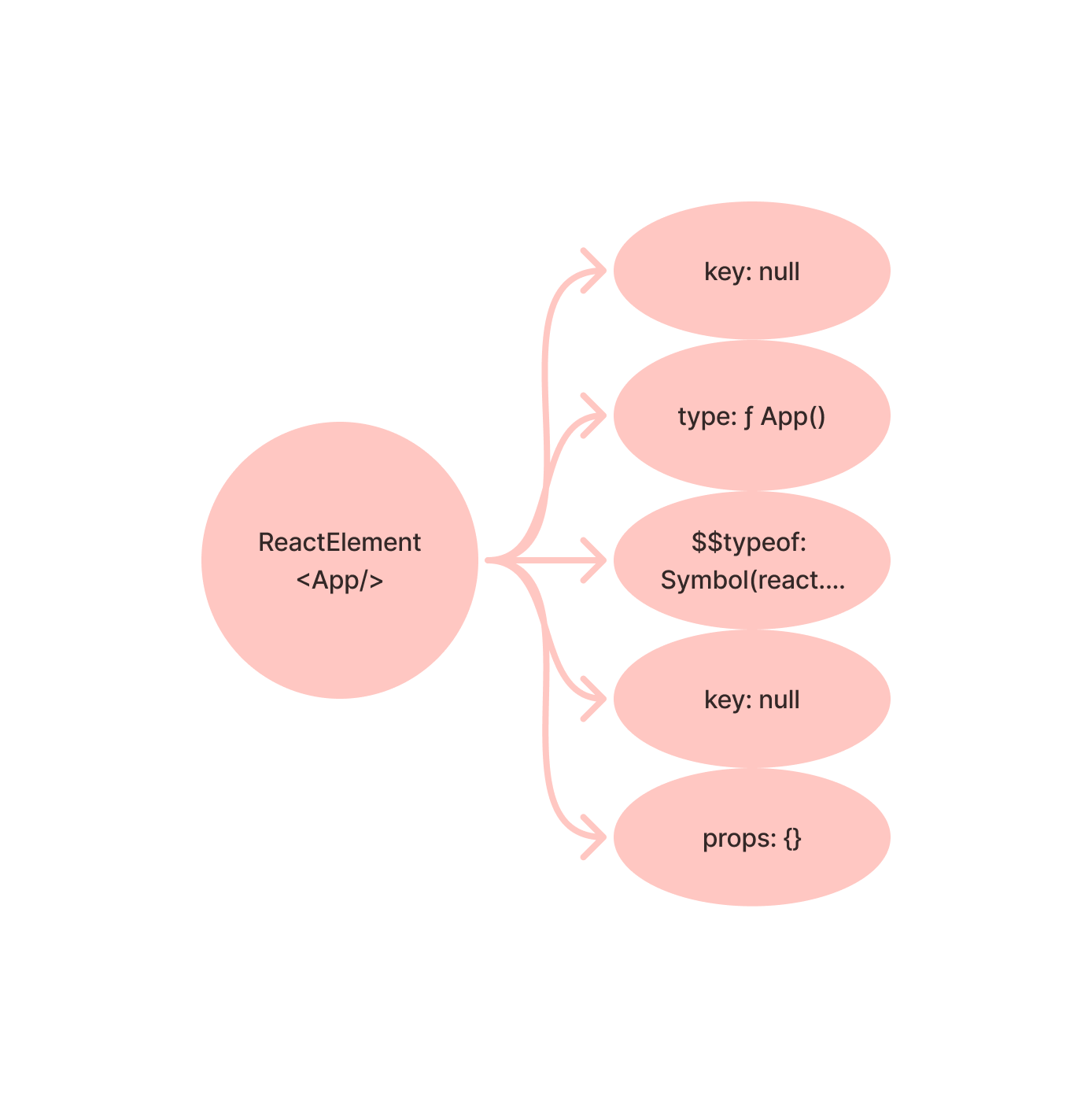
ReactDOMHydrationRoot.prototype.render = ReactDOMRoot.prototype.render =
function() {
const root = this._internalRoot;
updateContainer(children, root, null, null);
}
// packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberReconciler.js
function updateContainer(
element: ReactNodeList,
container: OpaqueRoot,
parentComponent: ?component(...props: any),
callback: ?Function,
): Lane {
const current = container.current;
const lane = requestUpdateLane(current);
updateContainerImpl(
current,
lane,
element,
container,
parentComponent,
callback,
);
return lane;
}
function updateContainerImpl(
rootFiber: Fiber,
lane: Lane,
element: ReactNodeList,
container: OpaqueRoot,
parentComponent: ?component(...props: any),
callback: ?Function,
): void {
const update = createUpdate(lane);
update.payload = {element};
// 这里会将 App ReactElement 插入队列.
// 将 update 加入 `updateQueue.shared.pending`(循环链表)。
const root = enqueueUpdate(rootFiber, update, lane);
if (root !== null) {
startUpdateTimerByLane(lane, 'root.render()', null);
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(root, rootFiber, lane);
entangleTransitions(root, rootFiber, lane);
}
}
render 方法内部调用 scheduleUpdateOnFiber(root, rootFiber, lane) 和 entangleTransitions(root, rootFiber, lane)。
调度阶段
scheduleUpdateOnFiber
scheduleUpdateOnFiber 是 React 调度更新的核心入口。当组件状态更新(如 setState、forceUpdate)时,该函数负责:
- 标记根节点有待处理的更新
- 根据更新优先级安排调度
- 处理渲染阶段更新和并发更新的边界情况
entangleTransitions
entangleTransitions 用于“纠缠”(entangle)多个 Transition 更新,确保它们在同一批次中一起处理,避免单独渲染导致不一致状态。
假设在一个 startTransition 中有多个 setState:
startTransition(()=>{
setState1();
setState2();
setState3();
});
entangleTransitions 会:
- 将
laneA、B、C 合并到sharedQueue.lanes - 标记根节点,使 A、B、C 必须一起处理
- 确保不会单独渲染其中某个更新
scheduleUpdateOnFiber 方法中会调用 ensureRootIsScheduled(root)。
根据 ensureRootIsScheduled 中的注释可以知道:ensureRootIsScheduled 确保根节点(Root)被加入调度队列,并确保有微任务来处理这个队列。当根节点收到更新时调用。
ensureRootIsScheduled 调用 scheduleImmediateRootScheduleTask。scheduleImmediateRootScheduleTask 用于在当前事件循环结束时,通过微任务(microtask)或立即任务处理所有待调度的根节点(Root),确保 React 更新在事件处理完成后统一调度。
// ReactFiberRootScheduler.js
function scheduleImmediateRootScheduleTask() {
if (supportsMicrotasks) {
scheduleMicrotask(() => {
processRootScheduleInMicrotask();
});
}
}
scheduleImmediateRootScheduleTask 中会调用 processRootScheduleInMicrotask。
function processRootScheduleInMicrotask() {
const currentTime = now();
let prev = null;
let root = firstScheduledRoot;
while (root !== null) {
const next = root.next;
const nextLanes = scheduleTaskForRootDuringMicrotask(root, currentTime);
if (nextLanes === NoLane) {
// This root has no more pending work. Remove it from the schedule. To
// guard against subtle reentrancy bugs, this microtask is the only place
// we do this — you can add roots to the schedule whenever, but you can
// only remove them here.
// Null this out so we know it's been removed from the schedule.
root.next = null;
if (prev === null) {
// This is the new head of the list
firstScheduledRoot = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
}
if (next === null) {
// This is the new tail of the list
lastScheduledRoot = prev;
}
} else {
// This root still has work. Keep it in the list.
prev = root;
// This is a fast-path optimization to early exit from
// flushSyncWorkOnAllRoots if we can be certain that there is no remaining
// synchronous work to perform. Set this to true if there might be sync
// work left.
if (
// Skip the optimization if syncTransitionLanes is set
syncTransitionLanes !== NoLanes ||
// Common case: we're not treating any extra lanes as synchronous, so we
// can just check if the next lanes are sync.
includesSyncLane(nextLanes) ||
(enableGestureTransition && isGestureRender(nextLanes))
) {
mightHavePendingSyncWork = true;
}
}
root = next;
}
}
processRootScheduleInMicrotask 方法中的关键步骤如下:
- 遍历调度队列:
- 从
firstScheduledRoot开始遍历所有根节点 - 对每个根节点调用
scheduleTaskForRootDuringMicrotask
- 从
- 移除没有工作的根节点:
- 如果
nextLanes === NoLane,说明没有待处理工作 - 从链表中移除该根节点
- 这是唯一可以移除根节点的地方(防止重入问题)
- 如果
- 更新同步工作标志:
- 如果根节点有同步工作,设置
mightHavePendingSyncWork = true - 用于优化
flushSync的性能
- 如果根节点有同步工作,设置
processRootScheduleInMicrotask 内会调用 scheduleTaskForRootDuringMicrotask。
function scheduleTaskForRootDuringMicrotask(
root: FiberRoot,
currentTime: number,
): Lane {
// 为根节点创建一个 Scheduler 任务,用于异步执行 React 的渲染工作。它是并发渲染的关键调度点。
const newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback(
schedulerPriorityLevel,
performWorkOnRootViaSchedulerTask.bind(null, root),
);
}
scheduleTaskForRootDuringMicrotask 的作用:
- 任务调度:为根节点安排渲染任务
- 优先级管理:确定下一个要处理的
lanes并映射到调度器优先级 - 过期处理:标记饥饿的
lanes为过期 - 同步/异步区分:同步工作直接刷新,异步工作通过调度器
- 任务复用:优先级未变时复用现有任务
- 挂起处理:正确处理
Suspended状态
这是 React 调度系统的核心函数,连接了 React 的优先级系统和浏览器的任务调度机制。
渲染阶段
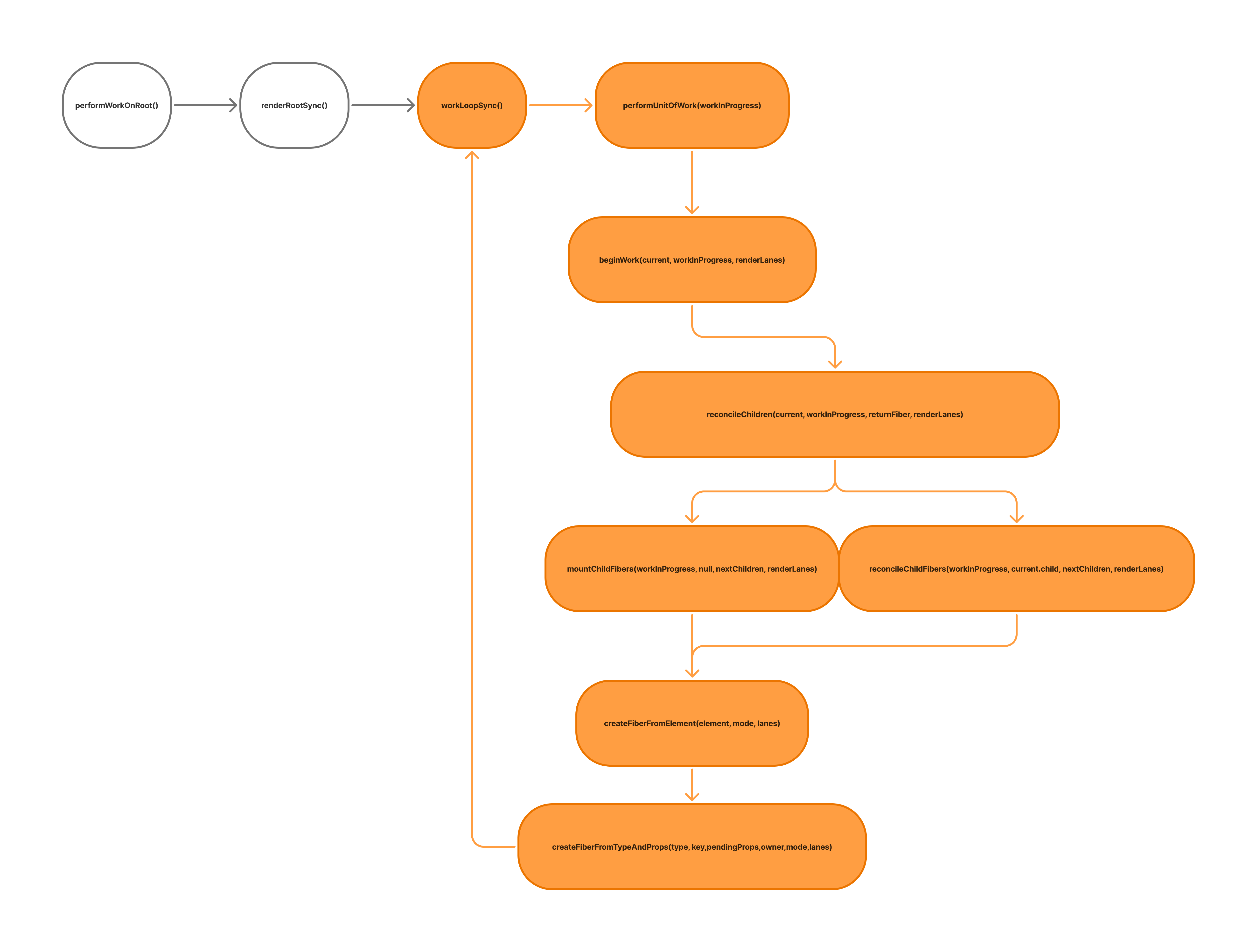
performWorkOnRootViaSchedulerTask 内部调用 performWorkOnRoot(root, lanes, forceSync) 进入工作循环。在进入工作循环之前,需要先设置 workInProgress。
function renderRootSync(
root: FiberRoot,
lanes: Lanes,
shouldYieldForPrerendering: boolean,
): RootExitStatus {
if (workInProgressRoot !== root || workInProgressRootRenderLanes !== lanes) {
prepareFreshStack(root, lanes);
}
workLoopSync();
}
prepareFreshStack(root, lanes) 中会通过 createWorkInProgress(current, pendingProps) 设置全局变量 workInProgress。此时的 workInProgress 指向根据 HostRootFiber 创建的 Fiber 节点。
prepareFreshStack 方法中调用 finishQueueingConcurrentUpdates() 将 updateContainerImpl() 期间暂存的并发更新添加到对应的 fiber/hook 队列中。
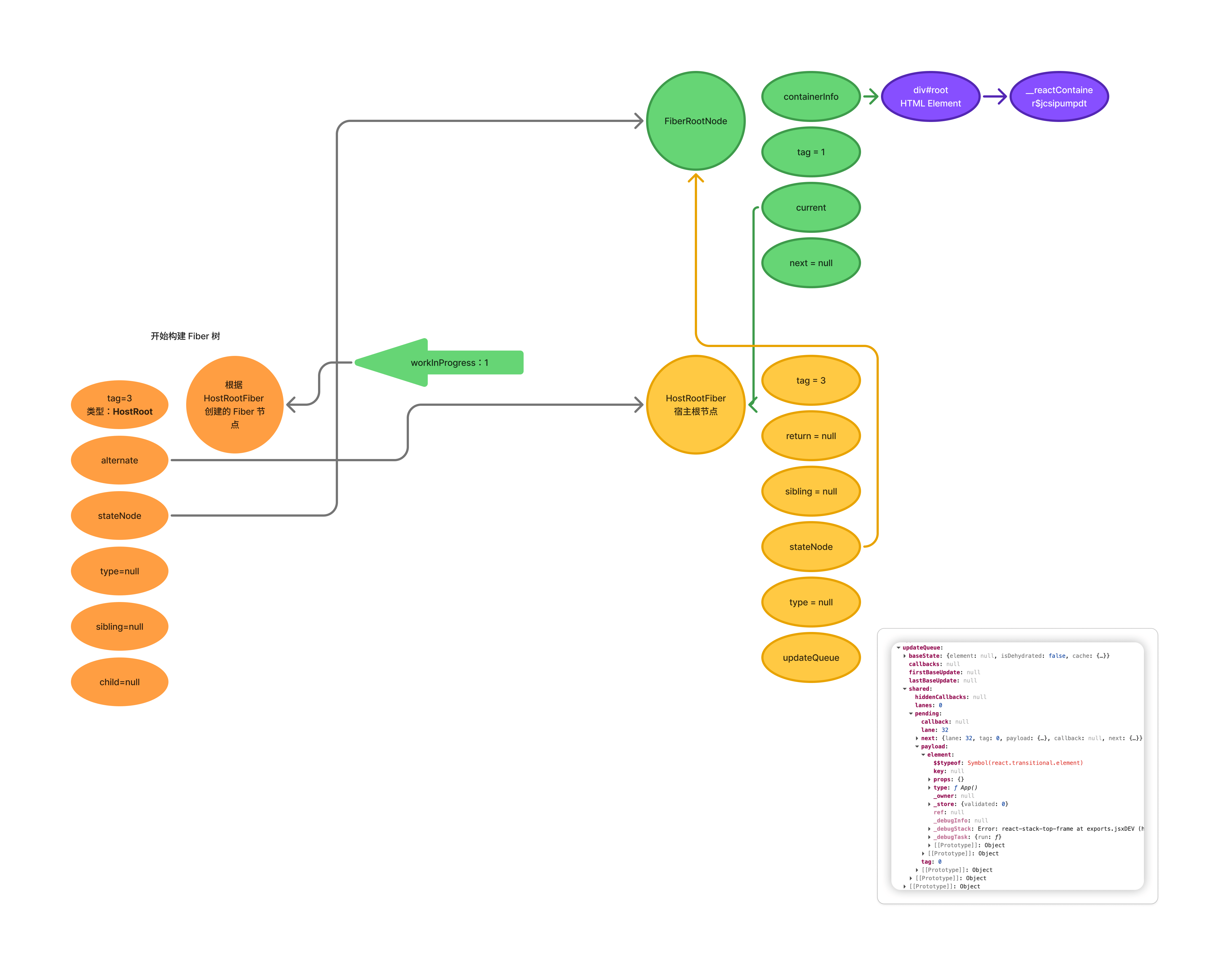
beginWork() 会根据 Fiber 节点的 tag 属性进行对应的处理。从 React 源码中可以找到不同的 tag 类型:
export const FunctionComponent = 0;
export const ClassComponent = 1;
export const HostRoot = 3; // Root of a host tree. Could be nested inside another node.
export const HostPortal = 4; // A subtree. Could be an entry point to a different renderer.
export const HostComponent = 5;
export const HostText = 6;
export const Fragment = 7;
export const Mode = 8;
export const ContextConsumer = 9;
export const ContextProvider = 10;
export const ForwardRef = 11;
export const Profiler = 12;
export const SuspenseComponent = 13;
export const MemoComponent = 14;
export const SimpleMemoComponent = 15;
export const LazyComponent = 16;
export const IncompleteClassComponent = 17;
export const DehydratedFragment = 18;
export const SuspenseListComponent = 19;
export const ScopeComponent = 21;
export const OffscreenComponent = 22;
export const LegacyHiddenComponent = 23;
export const CacheComponent = 24;
export const TracingMarkerComponent = 25;
export const HostHoistable = 26;
export const HostSingleton = 27;
export const IncompleteFunctionComponent = 28;
export const Throw = 29;
export const ViewTransitionComponent = 30;
export const ActivityComponent = 31;
workInProgress 上的 tag 属性为 3,说明是 HostRoot,beginWork 会将 workInProgress 转到处理 HostRoot 的逻辑上。
HostRoot 的处理由下面函数完成:
function updateHostRoot(
current: null | Fiber,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderLanes: Lanes,
) {
pushHostRootContext(workInProgress);
const nextProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
const prevState: RootState = workInProgress.memoizedState;
const prevChildren = prevState.element;
cloneUpdateQueue(current, workInProgress);
processUpdateQueue(workInProgress, nextProps, null, renderLanes);
const nextState: RootState = workInProgress.memoizedState;
const root: FiberRoot = workInProgress.stateNode;
pushRootTransition(workInProgress, root, renderLanes);
// being called "element".
const nextChildren = nextState.element;
// Root is not dehydrated. Either this is a client-only root, or it
// already hydrated.
resetHydrationState();
if (nextChildren === prevChildren) {
return bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
}
reconcileChildren(current, workInProgress, nextChildren, renderLanes);
return workInProgress.child;
}
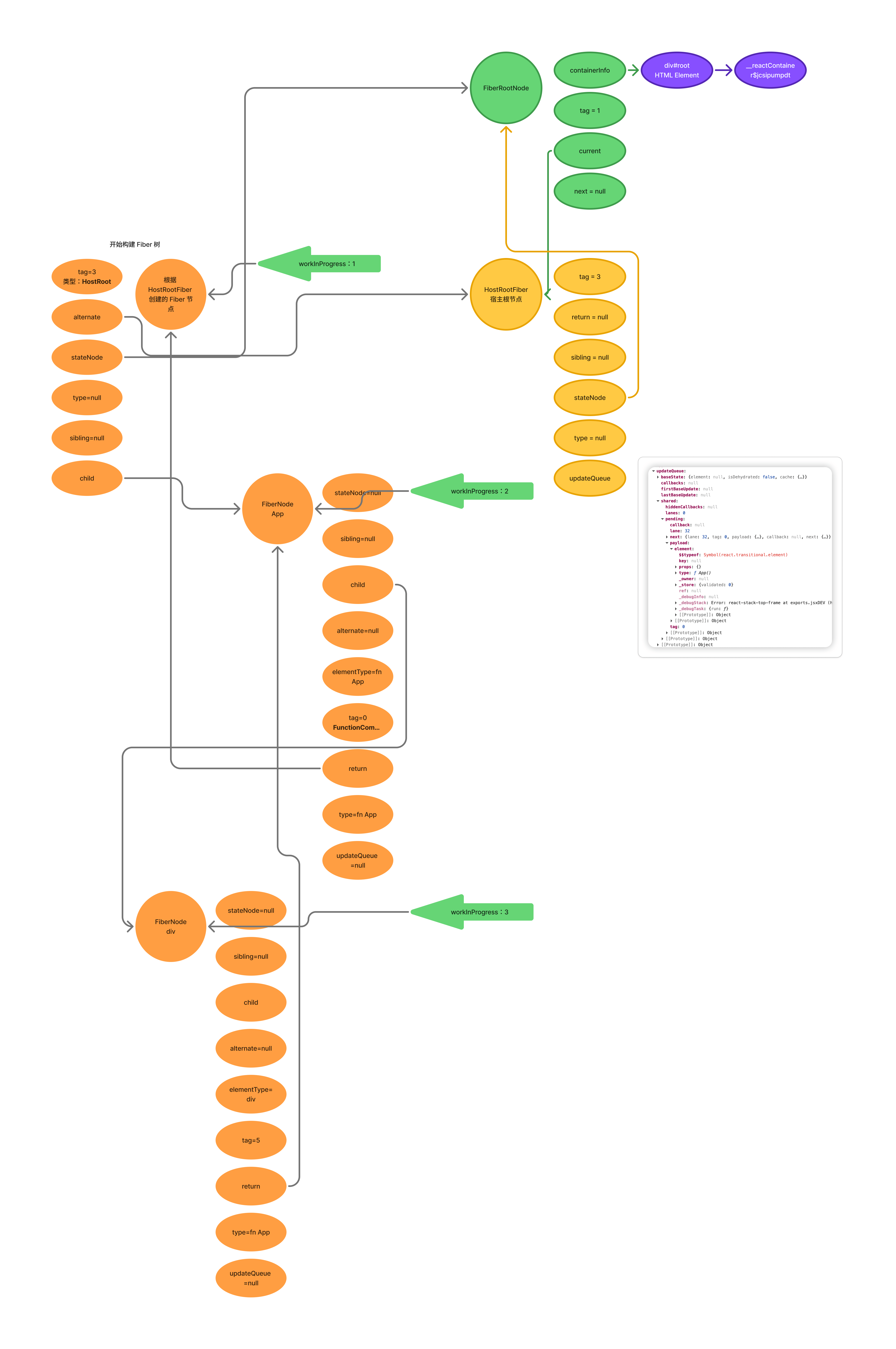
reconcileChildren 会给 child 属性赋值。child 指向的是 nextChildren 通过 createFiberFromElement 或 createFiberFromTypeAndProps 创建的 Fiber 节点。
至此第一轮循环结束,循环过程如下图:
下次循环中,workInProgress 指向 App 的 FiberNode。因为 workInProgress 的 tag 是 0,表示 Fiber 是函数组件,所以 beginWork 会调用 updateFunctionComponent() 进行处理。
updateFunctionComponent() 会使用 renderWithHooks 执行 App 函数,获得 App 函数中返回的 ReactElement 元素。之后将 ReactElement 元素交给 reconcileChildren 进行处理。
在 reconcileChildren 函数调用之前的 ReactElement 结构如下:
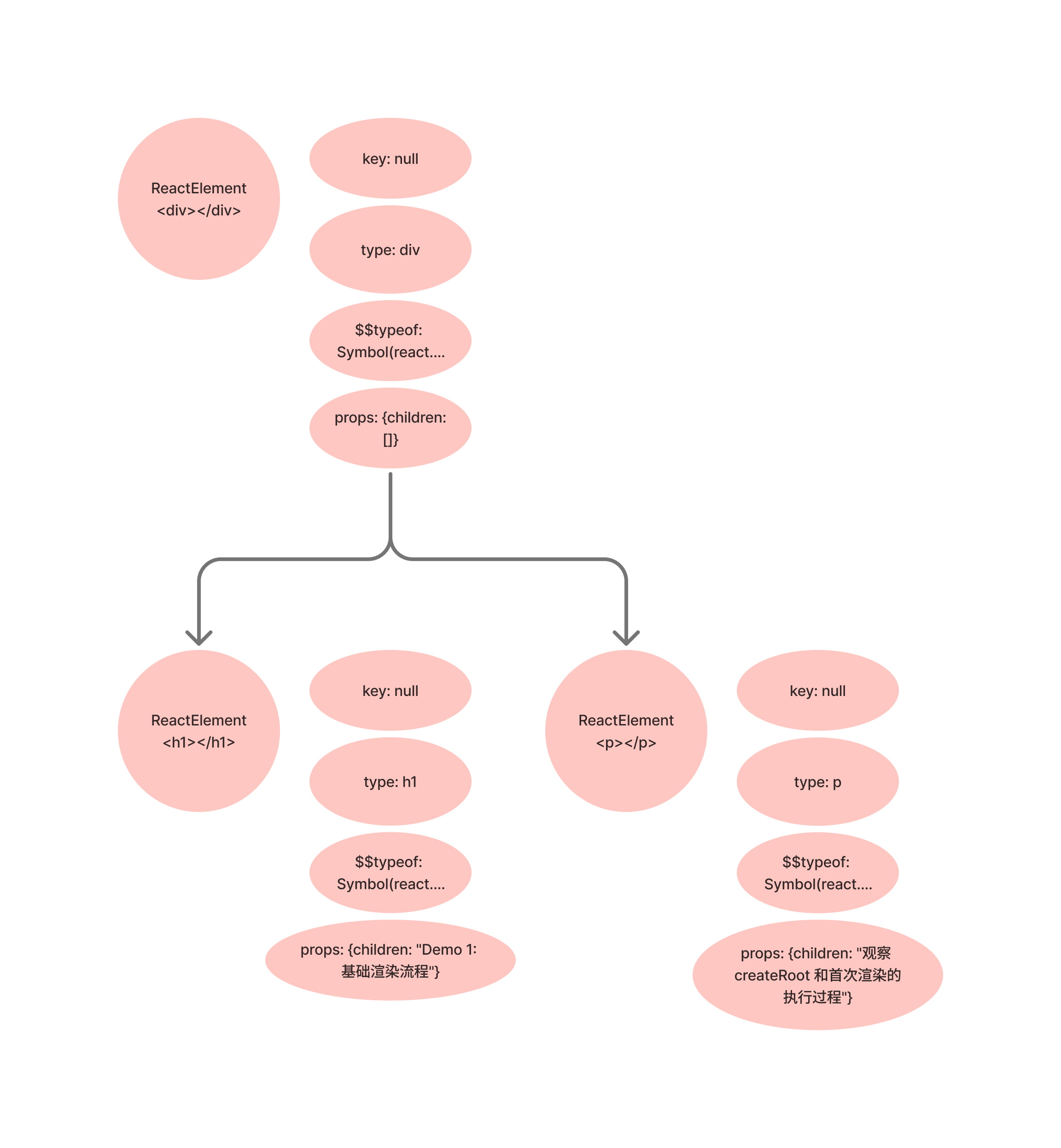
进入 reconcileChildren 创建 div ReactElement 的 FiberNode 节点:
下次循环中,workInProgress 指向 div 的 FiberNode,div FiberNode 的 pendingProps 属性表示了子节点。然后根据 pendingProps 进入子节点的构建。
由于 div 的 children 是数组,所以调用 reconcileChildrenArray 进行处理。
function reconcileChildrenArray(
returnFiber: Fiber,
currentFirstChild: Fiber | null,
newChildren: Array<any>,
lanes: Lanes,
): Fiber | null {
let resultingFirstChild: Fiber | null = null;
let previousNewFiber: Fiber | null = null;
for (let i = 0; i < newChildren.length; i++) {
const newFiber = updateSlot(returnFiber, oldFiber, newChildren[i], lanes);
if (previousNewFiber === null) {
resultingFirstChild = newFiber; // 第一个子节点
} else {
previousNewFiber.sibling = newFiber; // 设置 `sibling`
}
newFiber.return = returnFiber; // 设置 `return`
previousNewFiber = newFiber;
}
return resultingFirstChild; // 返回第一个节点
}
此时的 FibeNode 结构如下:
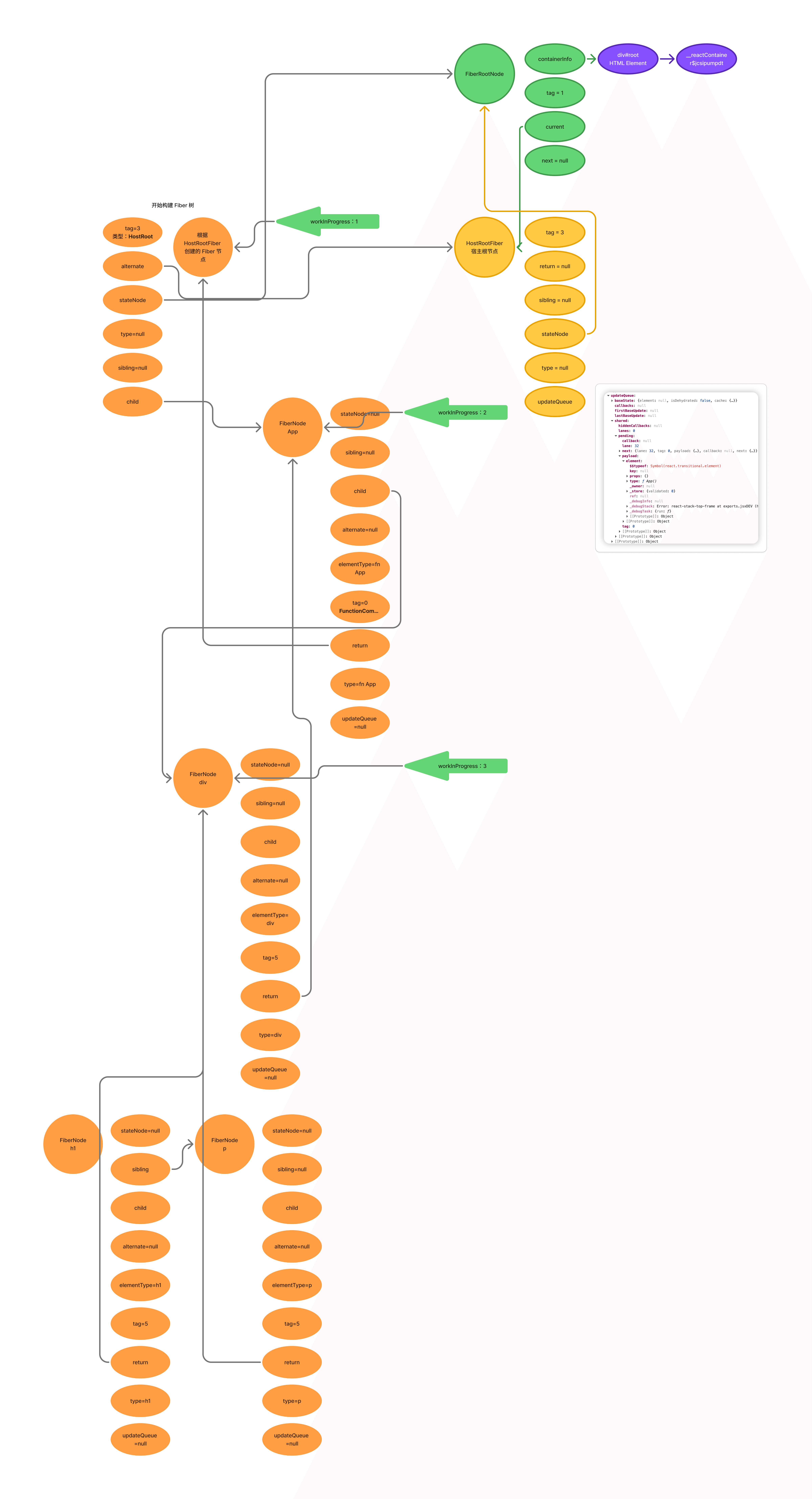
提交阶段
下次循环中,workInProgress 指向 H1 的 FiberNode。因为 H1 的 children 是文本,所以在 beginWork 中会把 flags 改为 Forked(Number(1048576).toString(2)) 。
因为 H1 已经没有子节点需要处理,所以会进入 completeUnitOfWork 阶段。在 complete 阶段,处理完 H1 的 DOM Element 后,会把 workInProgress 设置为兄弟节点 P。
由于 P 已经没有子节点需要处理,所以会进入 completeUnitOfWork 阶段。
function completeUnitOfWork(unitOfWork: Fiber): void {
let completedWork = unitOfWork;
do {
const current = completedWork.alternate;
const returnFiber = completedWork.return;
// completeWork: 完成当前节点的工作
completeWork(current, completedWork, renderLanes);
const siblingFiber = completedWork.sibling;
if (siblingFiber !== null) {
// 有兄弟节点,处理兄弟节点
workInProgress = siblingFiber; // 移动到兄弟节点
return;
}
// 没有兄弟节点,返回到父节点
completedWork = returnFiber;
workInProgress = completedWork; // 移动到父节点
} while (completedWork !== null);
}
completeWork 主要是创建 DOM 节点,设置插入 flags。对于 workInProgress 是 H1 FiberNode 的情况来说,completeWork 会将 H1 的 DOM Element 设置到 workInProgress.stateNode。
function completeWork(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderLanes: Lanes,
): null | Fiber {
const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case HostComponent:
// 创建 DOM 节点
const instance = createInstance(workInProgress.type, newProps);
workInProgress.stateNode = instance;
// 标记需要插入
workInProgress.flags |= Placement;
break;
// ... 其他类型
}
return null;
}
处理完 H1 和 P,开始向上回溯,到父 div 的 FiberNode。通过 nextResource.appendChild(_currentHostContext.stateNode); 把 h1 和 p 插入到新创建的 div 中。
completeWork 中会标记以下属性:
subtreeFlags子树标志(effects 等)改为Forked(Number(1048576).toString(2))childLanes子节点的lanes(更新优先级)NoFlagsflags设置为NoFlags
之后 workInProgress 指向 App 的 FiberNode。因为它是函数组件,所以 completeWork 中会标记两个属性:
actualDurationtreeBaseDurationsubtreeFlags子树标志(effects 等)改为Forked(Number(1048576).toString(2))childLanes子节点的lanes(更新优先级)NoFlagsflags设置为67108867即PerformedWork | Placement | PlacementDEV
workInProgress 为 HostRootFiber(即 App 的父级)时同样做上述处理。
subtreeFlags设置为68157443即PlacementDEV | SnapshotStatic | PerformedWork | PlacementchildLanes子节点的lanes(更新优先级)NoFlagsflags设置为1024即Snapshot
到此回溯完毕,设置 workInProgressRootExitStatus = RootCompleted。
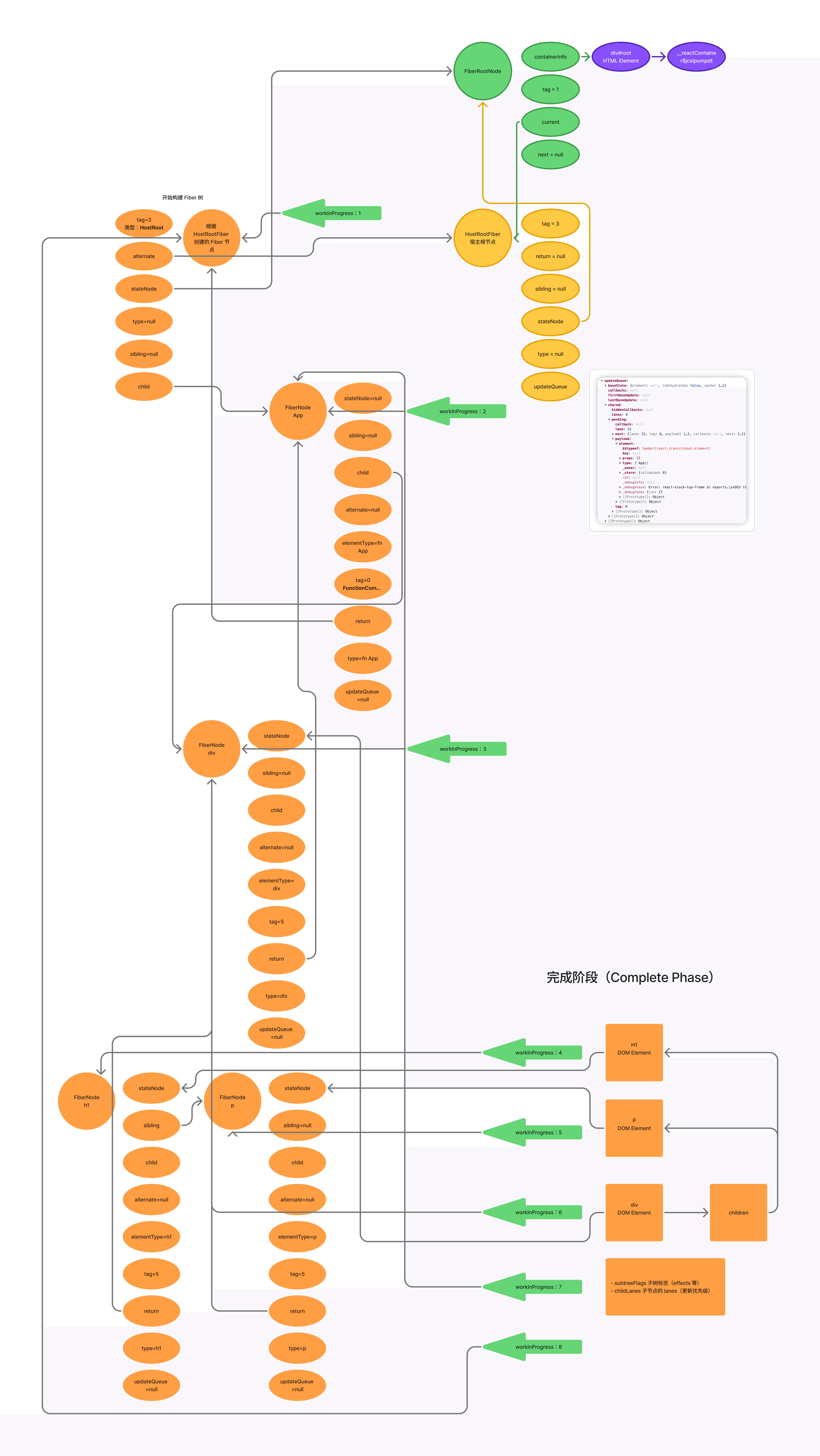
提交阶段
渲染完成后,检查是否可以提交:
function commitRootWhenReady(
root: FiberRoot,
finishedWork: Fiber,
// ...
) {
// 立即提交
commitRoot(/*...*/);
}
function commitRoot(
root: FiberRoot,
finishedWork: Fiber,
lanes: Lanes,
// ...
): void {
// 1. 刷新被动效果
flushPendingEffects();
// 2. 标记根节点完成
markRootFinished(root, lanes, remainingLanes);
// 3. 重置工作状态
workInProgressRoot = null;
workInProgress = null;
// Flush synchronously.
flushMutationEffects();
flushLayoutEffects();
// Skip flushAfterMutationEffects
flushSpawnedWork();
}
DOM 节点插入
flushMutationEffects() 中调用下面的方法处理 DOM 节点的插入:
function flushMutationEffects(): void {
commitMutationEffects(root, finishedWork, lanes);
// --commitMutationEffectsOnFiber(finishedWork, root, committedLanes);
// ----recursivelyTraverseMutationEffects(root, finishedWork, lanes);
// ------commitMutationEffectsOnFiber(child, root, lanes);
// --------commitReconciliationEffects(finishedWork);
// ----------commitHostPlacement(finishedWork);
// ------------commitPlacement(finishedWork);
root.current = finishedWork;
pendingEffectsStatus = PENDING_LAYOUT_PHASE;
}
function commitPlacement(finishedWork: Fiber): void {
// 1. 向上查找宿主父节点
let parentFiber = finishedWork.return;
while (parentFiber !== null) {
if (isHostParent(parentFiber)) {
hostParentFiber = parentFiber;
break;
}
parentFiber = parentFiber.return;
}
switch (hostParentFiber.tag) {
case HostRoot:
case HostPortal: {
// 2. 获取插入位置
const before = getHostSibling(finishedWork);
// 3. 插入节点
insertOrAppendPlacementNodeIntoContainer(
finishedWork,
before,
parent,
parentFragmentInstances,
);
}
}
}
function insertOrAppendPlacementNodeIntoContainer(
node: Fiber,
before: ?Instance,
parent: Container,
parentFragmentInstances: null | Array<FragmentInstanceType>,
): void {
const {tag} = node;
const isHost = tag === HostComponent || tag === HostText;
if (isHost) {
// 直接插入宿主节点
const stateNode = node.stateNode;
if (before) {
insertInContainerBefore(parent, stateNode, before);
} else {
appendChildToContainer(parent, stateNode);
}
return;
}
// 递归处理子节点
const child = node.child;
if (child !== null) {
insertOrAppendPlacementNodeIntoContainer(child, before, parent, /*...*/);
let sibling = child.sibling;
while (sibling !== null) {
insertOrAppendPlacementNodeIntoContainer(sibling, before, parent, /*...*/);
sibling = sibling.sibling;
}
}
}
页面渲染完毕,然后在 flushMutationEffects() 将 root.current 指向 FiberRoot。如下图中粉色区域进行了标注。
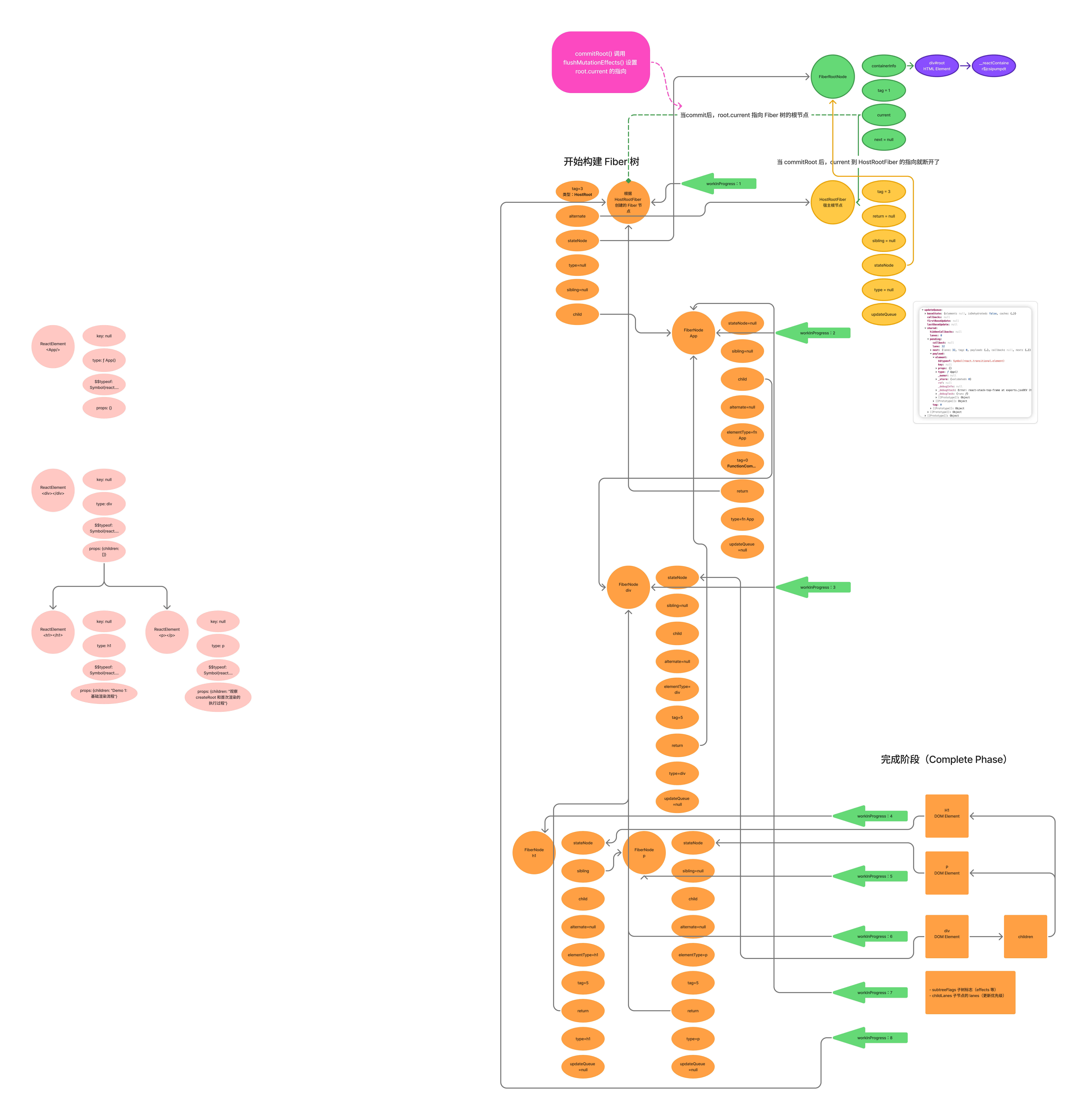
总结
React 的初始化流程可以概括为以下几个关键步骤:
- 创建阶段:创建
FiberRoot和根Fiber节点,初始化更新队列 - 调度阶段:将更新加入调度队列,通过微任务触发工作循环
- 渲染阶段
prepareFreshStack: 创建workInProgress树workLoop: 遍历Fiber树beginWork: 处理节点,构建子节点树completeWork: 完成节点,创建 DOM 节点
- 提交阶段
commitRootWhenReady: 检查是否可以提交commitRoot: 执行提交commitPlacement: 插入 DOM 节点
问题
每次在 prepareFreshStack 中都会创建一个新的 WIP 树吗?