React 状态更新流程
基于 v19.2.0 版本
本文将基于下述 Demo 来分析 React v19.2.0 的状态更新流程。
import { useState } from "react";
import { createRoot } from "react-dom/client";
function App() {
// 断点 1: useState 初始化
debugger;
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
// 断点 2: 组件渲染
console.log("渲染次数:", count);
const handleClick = () => {
// 断点 3: setState 调用
debugger;
setCount(count + 1);
// 断点 4: setState 调用后(注意:此时 count 还未更新)
debugger;
};
return (
<div>
<h1>状态更新流程</h1>
<p onClick={handleClick}>观察 setState 如何触发更新流程, {count}</p>
</div>
);
}
debugger;
const root = createRoot(document.getElementById("root"));
debugger;
root.render(<App />);
useState(0) 的执行过程
当创建 App Fiber 时,React 会先执行 renderWithHooks,然后调用 App 函数,从而触发 useState 的执行。
export function useState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
const dispatcher = resolveDispatcher();
// initialState = 0
return dispatcher.useState(initialState);
}
resolveDispatcher 会返回 packages/shared/ReactSharedInternals.js 中的 React.__CLIENT_INTERNALS_DO_NOT_USE_OR_WARN_USERS_THEY_CANNOT_UPGRADE,它实际上就是 ReactSharedInternals。
const ReactSharedInternals: SharedStateClient = ({
H: null,
A: null,
T: null,
S: null,
}: any);
ReactSharedInternals.H 会在 renderWithHooks 中被赋值:
function renderWithHooks() {
ReactSharedInternals.H = HooksDispatcherOnMountInDEV;
}
因此,resolveDispatcher 返回的是一个包含 useState 方法的对象。
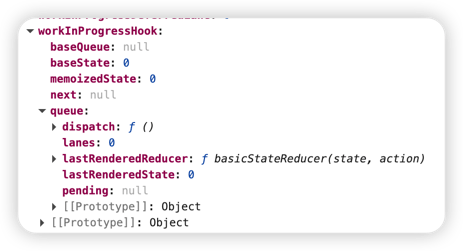
接下来,useState 方法会调用 mountState(initialState) 来设置 workInProgressHook,并将 workInProgressFiber 和 queue 绑定到 dispatchSetState,最后返回状态值和绑定后的 dispatch。
// The work-in-progress fiber. I've named it differently to distinguish it from
// the work-in-progress hook.
let currentlyRenderingFiber: Fiber = (null: any);
let workInProgressHook: Hook | null = null; // 存储当前的 Hooks
function mountState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S,
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
// hook 变量实际指向 workInProgressHook
const hook = mountStateImpl(initialState);
const queue = hook.queue;
const dispatch: Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>> = (dispatchSetState.bind(
null,
currentlyRenderingFiber,// workInProgressFiber
queue,
): any);
queue.dispatch = dispatch;
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}
function mountStateImpl<S>(initialState: (() => S) | S): Hook {
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
if (typeof initialState === 'function') {
const initialStateInitializer = initialState;
// $FlowFixMe[incompatible-use]: Flow doesn't like mixed types
initialState = initialStateInitializer();
if (shouldDoubleInvokeUserFnsInHooksDEV) {
setIsStrictModeForDevtools(true);
try {
// $FlowFixMe[incompatible-use]: Flow doesn't like mixed types
initialStateInitializer();
} finally {
setIsStrictModeForDevtools(false);
}
}
}
hook.memoizedState = hook.baseState = initialState;
const queue: UpdateQueue<S, BasicStateAction<S>> = {
pending: null,
lanes: NoLanes,
dispatch: null,
lastRenderedReducer: basicStateReducer,
lastRenderedState: (initialState: any),
};
hook.queue = queue;
return hook;
}
function mountWorkInProgressHook(): Hook {
const hook: Hook = {
memoizedState: null,
baseState: null,
baseQueue: null,
queue: null,
next: null,
};
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
// This is the first hook in the list
currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = hook;
} else {
// Append to the end of the list
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = hook;
}
return workInProgressHook;
}
workInProgressHook 的内存结构如下:
setCount(count + 1) 的执行过程
当点击 p 元素时,会触发 dispatchSetState 方法(该方法已经绑定了正确的 FiberNode 和 queue)。在本文的 demo 中,dispatchSetState 执行时,fiber 指向的是 App 的 FiberNode。
function dispatchSetStateInternal<S, A>(
fiber: Fiber,
queue: UpdateQueue<S, A>,
action: A,
lane: Lane,
): boolean {
const update: Update<S, A> = {
lane,
revertLane: NoLane,
gesture: null,
action,
hasEagerState: false,
eagerState: null,
next: (null: any),
};
const root = enqueueConcurrentHookUpdate(fiber, queue, update, lane);
if (root !== null) {
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(root, fiber, lane);
entangleTransitionUpdate(root, queue, lane);
return true;
}
}
enqueueConcurrentHookUpdate(fiber, queue, update, lane) 会找到需要更新的 Root。
然后通过 scheduleUpdateOnFiber 启动 Root(FiberRootNode)的调度。需要注意的是,此时的 scheduleUpdateOnFiber 不会调用 prepareFreshStack(root, NoLanes) 来创建新的 workInProgress,而是直接使用传递的参数 Root(FiberRootNode)。
// 通过 markRootUpdated 设置 pendingLanes
function markRootUpdated(root: FiberRoot, updateLane: Lane) {
root.pendingLanes |= updateLane;
}
此时 Root 的 pendingLanes 为 2。
与初次构造不同,状态更新不会直接调用 performSyncWorkOnRoot,而是通过调度中心(scheduler)来处理。不过,其调用链路 performSyncWorkOnRoot → renderRootSync → workLoopSync 与初次构造中的一致。
function renderRootSync(
root: FiberRoot,
lanes: Lanes,
shouldYieldForPrerendering: boolean
): RootExitStatus {
// If the root or lanes have changed, throw out the existing stack
// and prepare a fresh one. Otherwise we'll continue where we left off.
if (workInProgressRoot !== root || workInProgressRootRenderLanes !== lanes) {
prepareFreshStack(root, lanes);
}
outer: do {
try {
workLoopSync();
exitStatus = workInProgressRootExitStatus;
break;
} catch (thrownValue) {
handleThrow(root, thrownValue);
}
} while (true);
}
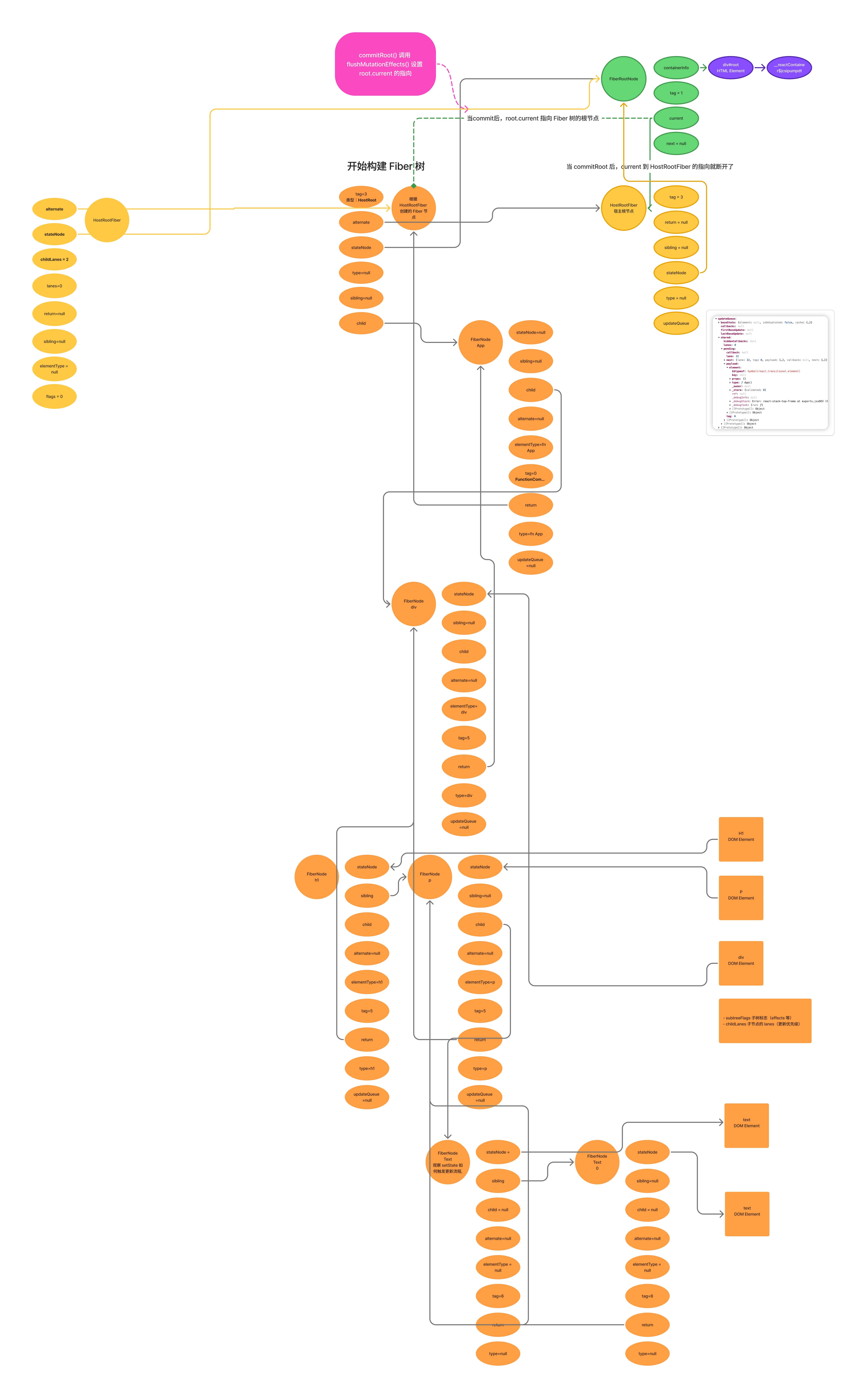
在进入 workLoopSync 前,会调用 prepareFreshStack 刷新栈帧。在 prepareFreshStack 中,会使用 root.current(HostFiberRoot)来创建 workInProgress。
此时的内存结构如下:
之后会进入 beginWork。在 beginWork 中,会检测 Fiber 是否有待处理的更新。如果 Fiber 有子树,还会检查子树是否有更新;如果子树存在更新,则返回子树的 FiberNode。
function beginWork(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderLanes: Lanes
): Fiber | null {
if (current !== null) {
const oldProps = current.memoizedProps;
const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
}
// 既没有 props 也没有 legacy context 变化。检查是否存在待处理的
// update 或 context 更新.
const hasScheduledUpdateOrContext = checkScheduledUpdateOrContext(
current,
renderLanes
);
if (
!hasScheduledUpdateOrContext &&
// 如果这是错误或 suspense boundary 的第二遍处理,可能
// 没有在 `current` 上调度工作,因此我们检查此标志。
(workInProgress.flags & DidCapture) === NoFlags
) {
// 没有待处理的更新或上下文。现在提前退出。
didReceiveUpdate = false;
return attemptEarlyBailoutIfNoScheduledUpdate(
current,
workInProgress,
renderLanes
);
}
}
function attemptEarlyBailoutIfNoScheduledUpdate(
current: Fiber,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderLanes: Lanes
) {
// 此 fiber 没有任何待处理的工作。提前退出而不进入
// begin 阶段。在这个优化路径中仍需要做一些簿记工作,
// 主要是将一些东西推入栈中。
return bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
}
function bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderLanes: Lanes
): Fiber | null {
if (current !== null) {
// Reuse previous dependencies
workInProgress.dependencies = current.dependencies;
}
// 检查子节点是否有任何待处理的工作。
if (!includesSomeLane(renderLanes, workInProgress.childLanes)) {
// 子节点也没有任何工作。我们可以跳过它们。
// TODO: 一旦我们重新添加 resuming,我们应该检查子节点是否是
// work-in-progress 集合。如果是,我们需要转移它们的 effects。
if (current !== null) {
// 在提前退出之前,检查子节点中是否有任何 context 变化。
lazilyPropagateParentContextChanges(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
if (!includesSomeLane(renderLanes, workInProgress.childLanes)) {
return null;
}
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 此 fiber 没有工作,但其子树有。克隆子
// fibers 并继续。
cloneChildFibers(current, workInProgress);
return workInProgress.child;
}
因为 workInProgress 上没有可调度的任务,所以 workInProgress 会指向 App FiberNode。
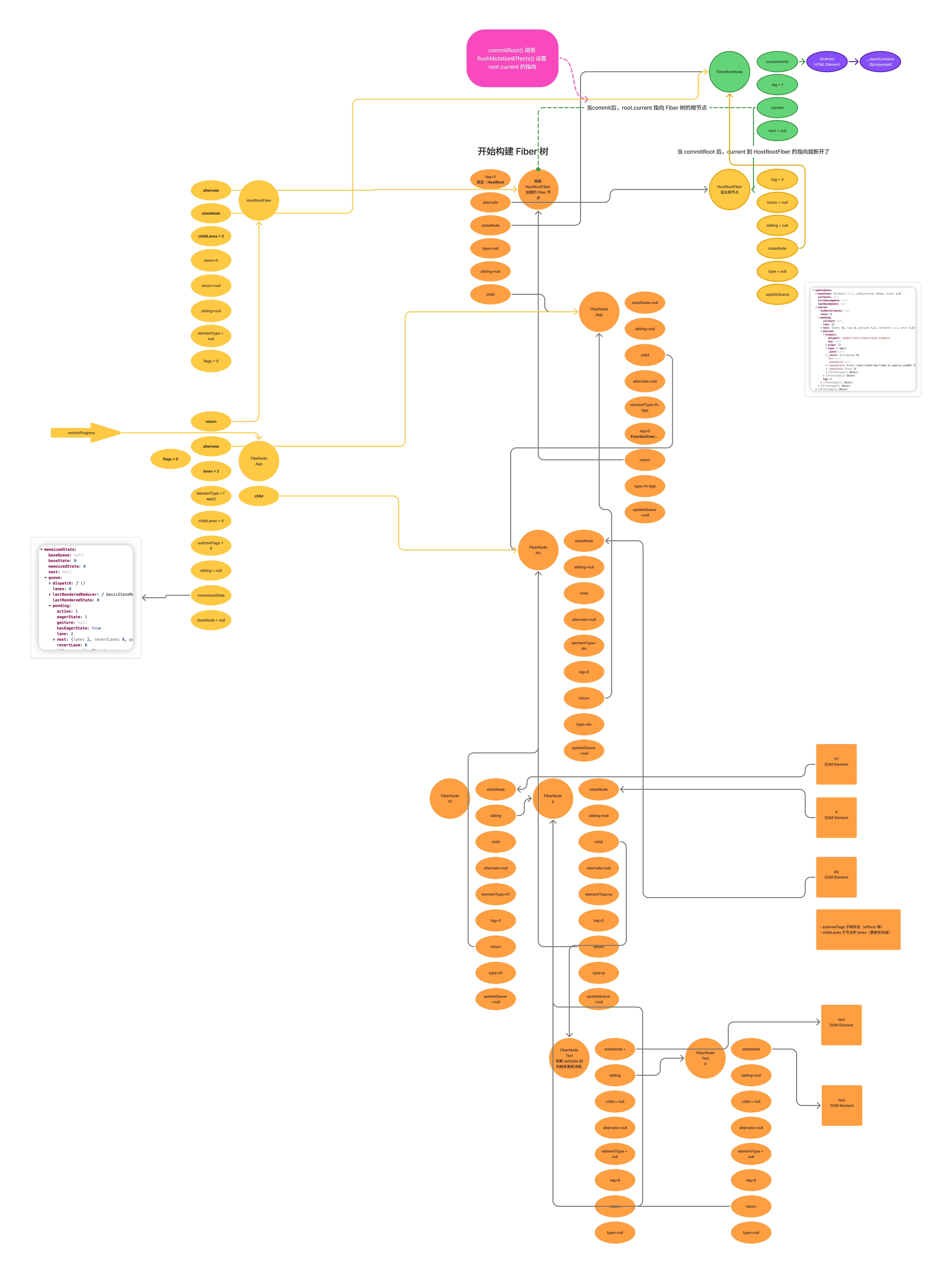
接下来进入 App FiberNode 的处理。此时 current 是 workInProgress.alternate。由于当前节点的 lanes != NoLanes,所以会调用 updateFunctionComponent 函数。
在 updateFunctionComponent 函数中,调用 App 内的 useState 会获取 memoizedState 经过计算后的最新值 1,之后创建 ReactElement,并调用 reconcileChildren() 生成下级子节点。
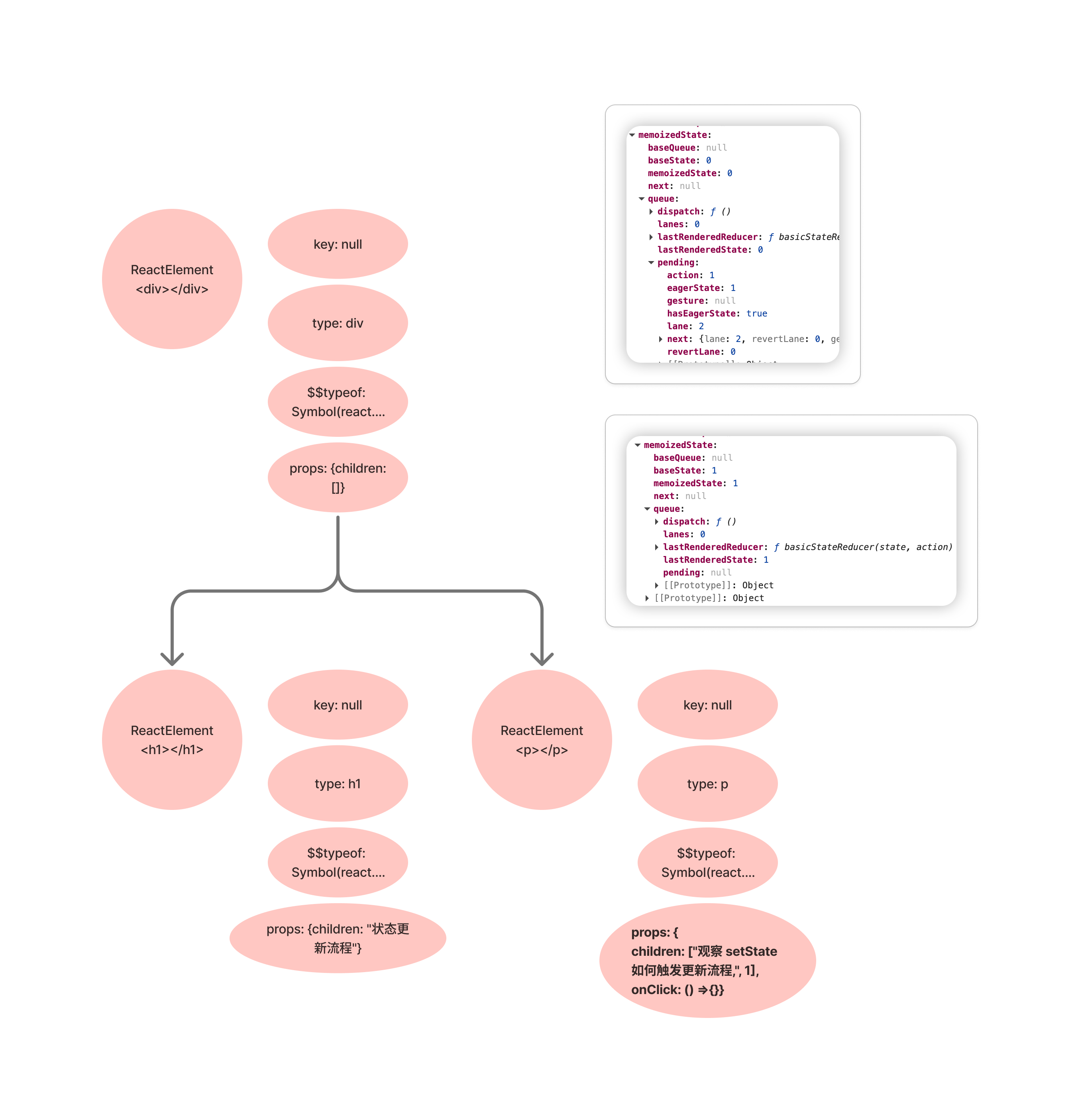
App FiberNode 处理结束后,下轮循环中,workInProgress 指向 div FiberNode。
当处理到 p 下的第一个子 FiberNode 时,
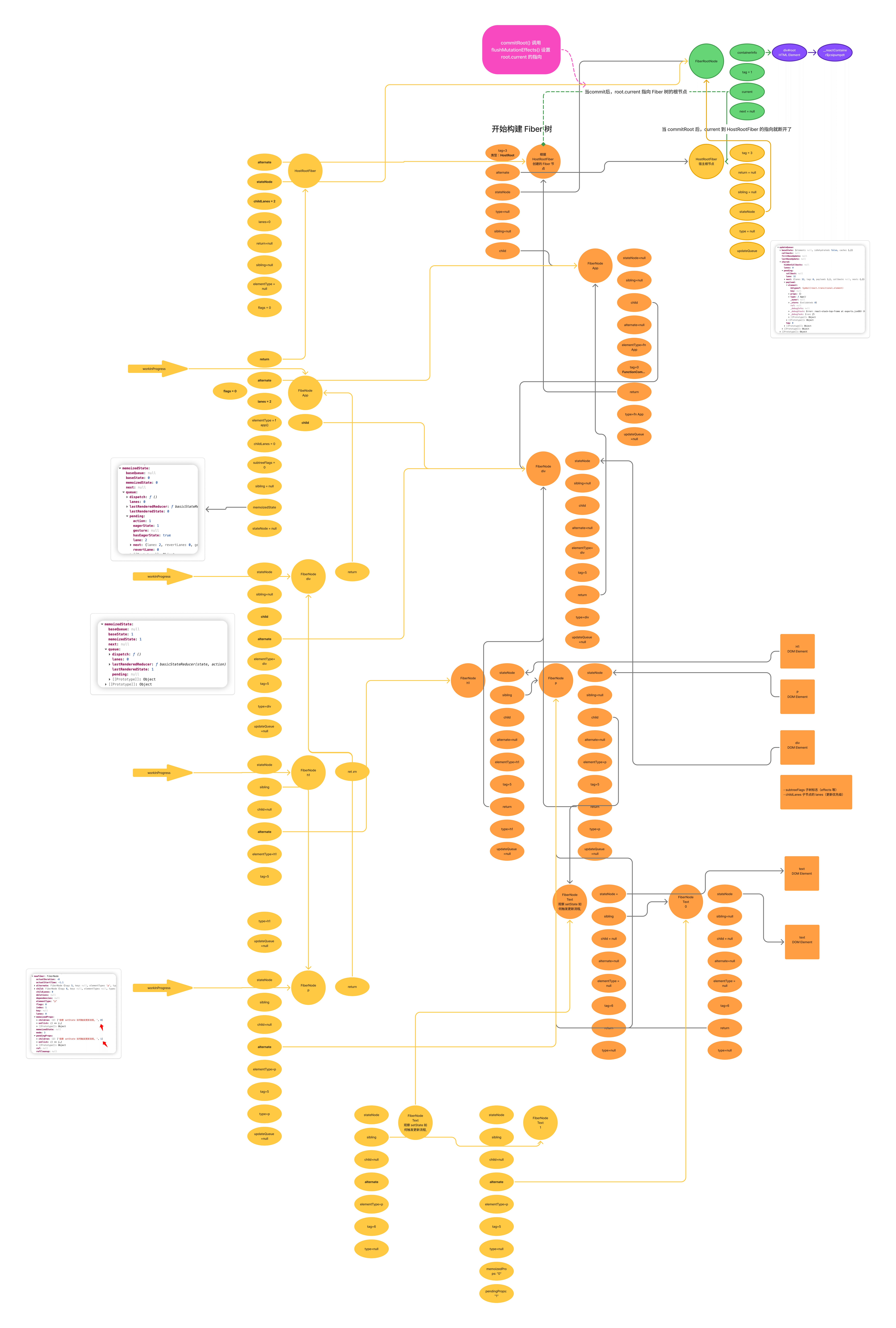
因为没有变更,所以会提前退出,进入 completeUnitOfWork。由于 FiberNode.memoizedProps === newProps,所以不会标记更新。
接下来,workInProgress 指向 p 下的第二个子 FiberNode。在 beginWork 中会判断 current.memoizedProps !== workInProgress.pendingProps。由于 current.memoizedProps 为 0,而 workInProgress.pendingProps 为 1,所以会设置 didReceiveUpdate 为 true,不会提前退出。
后面没有可以处理的子节点,所以进入 completeWork 阶段。由于 FiberNode.memoizedProps !== newProps,会通过 markUpdate(workInProgress) 标记更新(将 workInProgress.flags 设置为 Update)。
注意:此时的 workInProgress 为 p 下的第二个子 FiberNode。
function markUpdate(workInProgress: Fiber) {
workInProgress.flags |= Update;
}
回溯到 p 的 FiberNode,由于 FiberNode.memoizedProps !== newProps,会通过 markUpdate(workInProgress) 标记更新(将 workInProgress.flags 设置为 Update)。
回溯到 div 的 FiberNode,同样因为 FiberNode.memoizedProps !== newProps,会通过 markUpdate(workInProgress) 标记更新。
回溯到 App 的 FiberNode,会修改 subtreeFlags 和 childLanes,这两个属性的值是根据子节点的对应属性进行位运算得出的。
回溯到 Root 的 FiberNode,同样会修改 subtreeFlags 和 childLanes,这两个属性的值也是根据子节点的对应属性进行位运算得出的。
至此,回溯节点过程结束,准备进入渲染阶段。
渲染阶段的工作由 commitMutationEffectsOnFiber 方法完成:
function commitMutationEffects(
root: FiberRoot,
finishedWork: Fiber,
committedLanes: Lanes
) {
commitMutationEffectsOnFiber(finishedWork, root, committedLanes);
}
function commitMutationEffectsOnFiber(
finishedWork: Fiber,
root: FiberRoot,
lanes: Lanes
) {
const prevEffectStart = pushComponentEffectStart();
const prevEffectDuration = pushComponentEffectDuration();
const prevEffectErrors = pushComponentEffectErrors();
const prevEffectDidSpawnUpdate = pushComponentEffectDidSpawnUpdate();
// 获取当前 fiber 的 alternate(用于对比)
const current = finishedWork.alternate;
// 获取 fiber 的 flags(标记需要执行的副作用)
const flags = finishedWork.flags;
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
case FunctionComponent:
case ForwardRef:
case MemoComponent:
case SimpleMemoComponent: {
recursivelyTraverseMutationEffects(root, finishedWork, lanes);
commitReconciliationEffects(finishedWork, lanes);
if (flags & Update) {
commitHookEffectListUnmount(
HookInsertion | HookHasEffect,
finishedWork,
finishedWork.return
);
// TODO: Use a commitHookInsertionUnmountEffects wrapper to record timings.
commitHookEffectListMount(HookInsertion | HookHasEffect, finishedWork);
commitHookLayoutUnmountEffects(
finishedWork,
finishedWork.return,
HookLayout | HookHasEffect
);
}
break;
}
case HostText: {
recursivelyTraverseMutationEffects(root, finishedWork, lanes);
commitReconciliationEffects(finishedWork, lanes);
if (flags & Update) {
if (supportsMutation) {
if (finishedWork.stateNode === null) {
throw new Error(
"This should have a text node initialized. This error is likely " +
"caused by a bug in React. Please file an issue."
);
}
const newText: string = finishedWork.memoizedProps;
// For hydration we reuse the update path but we treat the oldProps
// as the newProps. The updatePayload will contain the real change in
// this case.
const oldText: string =
current !== null ? current.memoizedProps : newText;
commitHostTextUpdate(finishedWork, newText, oldText);
}
}
break;
}
}
popComponentEffectStart(prevEffectStart);
popComponentEffectDuration(prevEffectDuration);
popComponentEffectErrors(prevEffectErrors);
popComponentEffectDidSpawnUpdate(prevEffectDidSpawnUpdate);
}
recursivelyTraverseMutationEffects 会递归处理子节点:先处理删除(deletions),再递归处理子节点。
commitReconciliationEffects 处理协调相关副作用:处理 Placement(插入/重新排序)、处理 Hydrating(hydration 相关)。
在 case 中,除了调用这两个方法外,还会根据 flags 处理特定副作用:
- Update:更新相关副作用
- Ref:ref 的附加/分离
- ContentReset:内容重置
- FormReset:表单重置
- 其他特定 flag